RFID UHF Antenna Classification
發(fā)布時(shí)間:2022-08-03 09:15:46
RFID antenna is a very important part of hardware equipment in RFID reading, the different antennas directly affect the reading distance and range. RFID antennas are of various types, how to choose the right antenna according to different projects is very important.



According to different materials
There are PCB antenna, ceramic antenna, aluminum plate antenna and FPC antenna, etc.. Each material has its advantages and disadvantages and is used in different scenarios. Such as ceramic antenna, it has stable performance and small size. We know that the smallest size of ceramic antenna is 1818 mm, of course, there may be smaller ones. But the ceramic antenna is not suitable to do too large, the largest on the market is 6dBi, size 120*120mm. If the size is relatively large, both production and cost are not as advantageous as PCB and aluminum antenna. PCB and aluminum plate antennas are large gain antennas and are the choice of most people. For PCB antennas and alumimum antennas, the shell can be installed to meet the outdoor use. The biggest characteristic of FPC antenna is flexible, suitable for almost all small electronic products.
The difference between circularly polarized and linearly polarized antennas
For linear polarization, when the polarization direction of the receiving antenna is consistent with the linear polarization direction (the direction of the electric field), the signal is the best (the projection of the electromagnetic wave in the polarization direction is the largest). On the contrary, as the polarization direction of the receiving antenna is more different from the linear polarization direction, the signal becomes smaller (the projection decreases continuously). When the polarization direction of the receiving antenna is orthogonal to the linear polarization direction (magnetic field direction), the signal induced is zero (projection is zero). The linear polarization method has higher requirements on the direction of the antenna. Linearly polarized antennas are rarely used, for example, the antennas in microwave anechoic chamber experiments must be linearly polarized antennas.
For circularly polarized antennas, the induced signal is the same regardless of the polarization direction of the receiving antenna, and there is no difference (the projection of electromagnetic waves in any direction is the same). Therefore, the use of circular polarisation makes the system less sensitive to the orientation of the antenna (here the orientation is the orientation of the antenna, which is different from the orientation of the directional system mentioned earlier). Therefore,circularly polarised antennas are used in most situations in IoT projects.


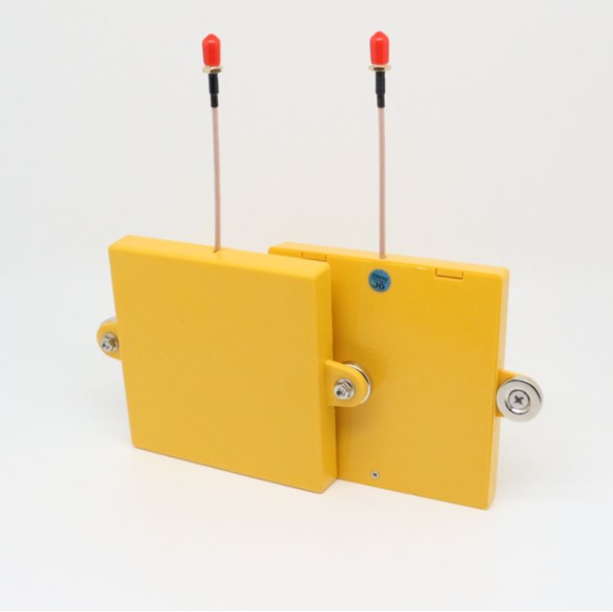
The difference between near-field antennas and far-field antennas
As the name implies, near-field antenna is an antenna for close-range reading. The energy radiation is concentrated in the relatively close range above the antenna, which ensures the close-range reading effect without misreading or string reading the surrounding electronic tags. Its applications are mainly aimed at projects that need to be read at close range without misreading the tags around the antenna, such as jewelry inventory management, medical equipment management, unmanned supermarket settlement, and smart tool cabinets and so on.
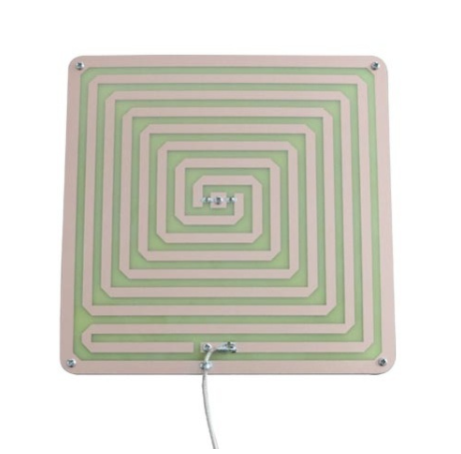


The far-field antenna has a large energy radiation angle and a long distance. With the increase of antenna gain and size, the radiation range and reading distance increase accordingly. In application, all the far-field antennas are needed for remote reading, and the handheld reader also use far-field antennas. For example, warehouse logistics management, factory material control and asset inventory, etc.



The far-field antenna has a large energy radiation angle and a long distance. With the increase of antenna gain and size, the radiation range and reading distance increase accordingly. In application, all the far-field antennas are needed for remote reading, and the handheld reader also use far-field antennas. For example, warehouse logistics management, factory material control and asset inventory, etc.